Legacy Documentation¶
This section describes the legacy interface using the File class. This interface is maintained for backward compatibility.
Getting log data¶
from lammps_logfile import File
import os
# We are in docs/api_reference/legacy/python
# We need to go up to api_reference, then docs, then root, then examples/logfiles/crack_log.lammps
# That is ../../../../examples/logfiles/crack_log.lammps
Now the arrays t and temp contain the log data corresponding to the Time and Temp columns in the log file.
Plotting log data¶
t = log.get("Time")
temp = log.get("Temp")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(t, temp)
To make the plot pop up in a window rather than being saved to a file, run plt.show() rather than plt.savefig(...).
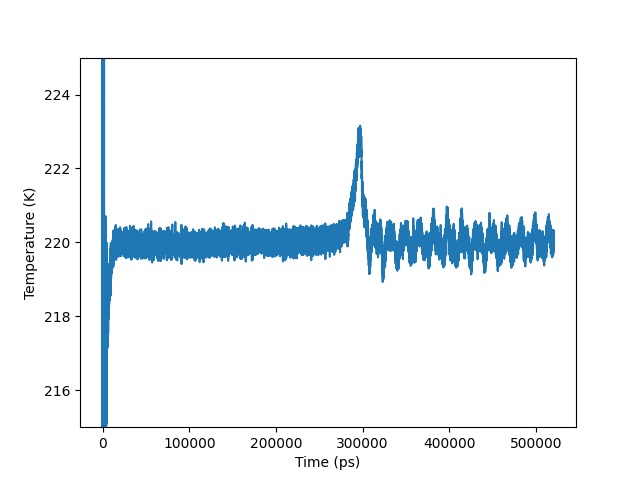
Plot of temperature vs. time¶
Running average¶
plt.ylabel("Temperature (K)")
plt.ylim([215, 225])
plt.savefig("time_temp.png")
from lammps_logfile import running_mean
temp_avg = running_mean(temp, 100)
plt.plot(t, temp_avg)
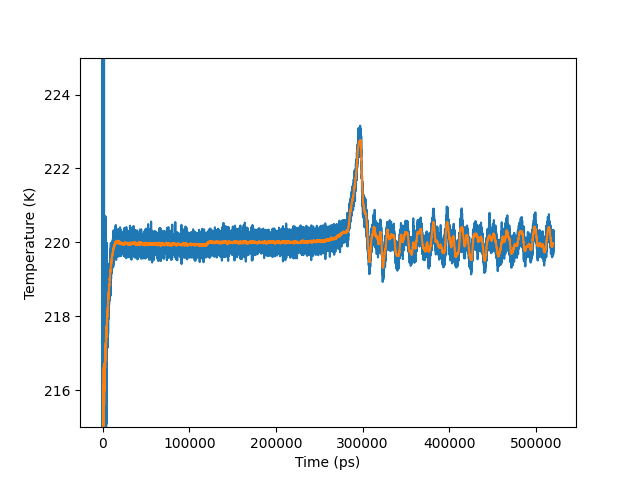
Plot of temperature vs. time. The blue curve is the raw output, whereas in the orange curve the temperature has been smoothed over a 100 log entries wide averaging window.¶
What data are available in the log file?¶
To inspect what columns are available, you can run the get_keywords-method on the File object:
print(log.get_keywords())
This command yields an output like the one below, which shows what columns we may get from the File object:
['Density', 'E_angle', 'E_bond', 'E_coul', 'E_dihed', 'E_impro', 'E_long', 'E_vdwl', 'KinEng', 'Lx', 'Ly', 'Lz', 'PotEng', 'Press', 'Pxx', 'Pxy', 'Pxz', 'Pyy', 'Pyz', 'Pzz', 'Step', 'Temp', 'Time', 'TotEng', 'methaneM', 'waterMsd']
Legacy File API¶
- class File(ifile)¶
Bases:
objectClass for handling lammps log files.
- Parameters:
ifile (str or file) – Path to lammps log file or a file-like object.
- flush_dict_and_set_new_keyword(keywords)¶
- get(entry_name, run_num=-1)¶
Get time-series from log file by name.
If the rows in the log file changes between runs, the logs are being flushed.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Array containing the requested data, or None if the entry is not found.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- get_keywords(run_num=-1)¶
Return list of available data columns in the log file.
- get_num_partial_logs()¶
Returns the number of partial logs (runs) found in the file.
- Returns:
Number of runs.
- Return type:
- property names¶
Exposes the keywords returned by get_keywords.
- Returns:
List of keywords.
- Return type:
- read_file_to_dict()¶